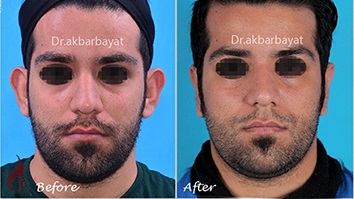
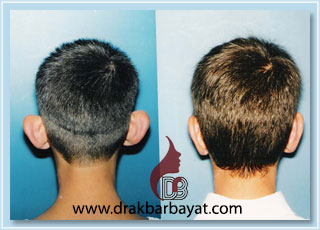
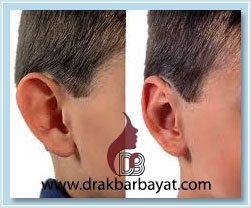
Just like other parts of the face, ears have great impact on facial beauty. Otapostasis, also known as prominent ear, protruding ear, or bat ear, is an important factor contributing to having visually unattractive ears. This condition sometimes gives other people a reason to make fun of the affected individual. Most people with otapostasis try to cover their ears by wearing long hair. While this can be done more easily by women, wearing long hair is not as easy for men.

What is otapostasis?
While different people have different shapes of ears, a feature of a normal ear is its harmony with other parts of the face. Ears are normally placed at a 25-30 degree angle with respect to the skull. The rim of the ear is almost 15-20 mm away from the skull. A greater angle or distance creates what we call otapostasis. The condition is often bilateral, although unilateral cases are also found in some individuals.
What are the causes of otapostasis and how can I prevent them?
Protruding ear has genetic causes which are rooted in dominant genes. For infants with otapostasis, special splints or molds are used to prevent the deformity as infants have soft auricle.
However, this is usually effective within three weeks from birth, and loses its effect once the baby grows older. It should also be noted that special care must be taken to prevent excessive pressure on the ear as this can cause the ears to shrink. Remember that otapostasis is more common among children under 2 to 3 years of age. The condition is often automatically corrected at later stages with no requirement for treatment. Auricle usually reaches full development at the age of 6, and at later stages, no improvement will be seen unless some treatment takes place.
What are the complications caused by otapostasis?
Fortunately, people with otapostasis have completely normal hearing. On the other hand, their IQ is just as normal as other individuals. Some of them have even higher-than-average IQ. Important undesirable effects of otapostasis include psychological distress and lack of self-confidence in social activities.
How is it corrected?
Otapostasis can be corrected through outpatient surgical procedures. This is done with topical anesthesia. However, general anesthesia is used for children or those individuals who are afraid of surgery. A cut is made behind the ear to remove a part of the cartilage and reshape the ear. The affected area will be completely restored to normal condition and is often unnoticeable due to its location. The procedure has no impact on hearing.
What is the proper age for surgery?
Surgery is performed once the cartilage is fully developed (when the individual is 6 or older). The results have been almost equally satisfactory both in children and adults. However, early correction will help children regain their self-confidence and sociability.
How is the post-surgical recovery?
The surgery consists of simple procedures and, as mentioned earlier, is an outpatient surgery. You won’t need to rest at home as you will be able to go to school or work the day after the surgery.
What types of care should be taken after surgery?
- A soft dressing is applied to the ears, which should remain for 2-3 days.
- The patient needs to take a bath on daily basis and wash the affected area with water and soap.
- Medications are prescribed for reducing pain and preventing infections.
- Headbands should be used during sleep for a week.
- The ears must be protected against hits or stretches for 6 to 12 months.